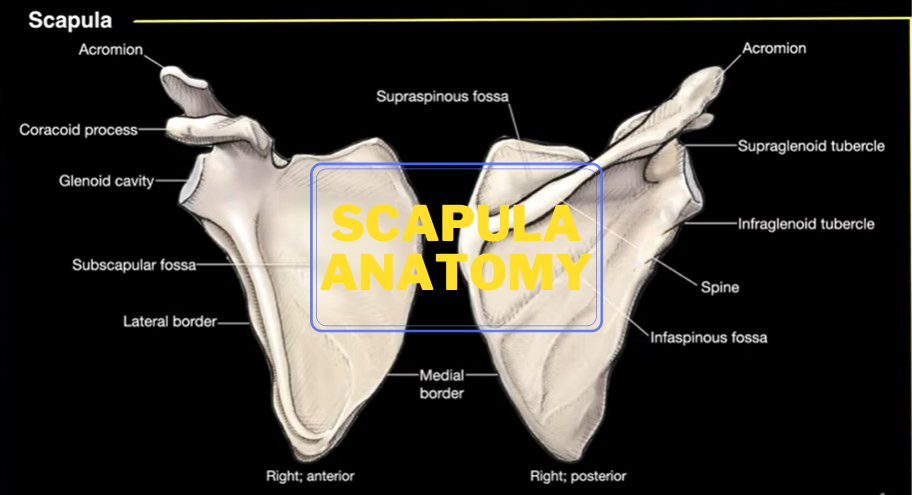
Let’s talk about the scapula and answer the question what is the scapula? What are its primary bony landmarks?
What is Scapula?
The Scapula also called the shoulder blade lies on the posterior part of the body. The scapula is a flat triangular bone placed in the thoracic cage (human rib cage).
Extending from the level of the second rib to the seventh rib. It provides support to the muscles of the forelimb. Articulation for the humerus (upper arm bone) at the glenoid cavity and it is joined to the clavicle in front.
The scapula or shoulder blade is a major bony component of the shoulder and functions to connect the upper extremity with the trunk of the body.
The scapula articulates with two other bones:
- Laterally with the humerus at the glenoid cavity.
- Superiorly with the clavicle at the acromial process.
Side Determination of Scapula:
How do we determine the side of the scapula? Basically, the spinous process should always face backward. The glenoid cavity should face laterally that is away from the body.
The lateral border is always thick while the medial border is thin.
Anatomical Features of the Scapula:
Surfaces:
The costal surface is concave and it faces the thoracic cage. It has three longitudinal ridges and gives attachment to the intermuscular septa. There is another thick ridge adjoining the lateral border. This part of the bone is almost rod-like. It acts like a lever for the action of the serratus anterior in the overhead abduction of the arm.
The dorsal surface gives attachment to the spine of the scapula which divides the surface into a smaller supraspinous fossa and a larger infraspinous fossa. The two fossa are connected to each other by the spinal glenoid notch. It is situated between the spine of the scapula and the glenoid angle.
Angle:
The angle includes the superior angle, inferior angle, and lateral angle.
- The superior angle is covered by the trapezius.
- The inferior angle is covered by the latissimus dorsi and it lies just opposite to the superior angle it moves forwards around the chest. When the arm is abducted.
- The lateral angle or the glenoid angle faces laterally and away from the body.
Borders:
- The medial border is the longest and faces the vertebral column. It’s on the medial side of the bone, so it’s called the medial border of the scapula. It’s also the border that is closest to the vertical column, so it’s also called a “vertebral border”.
- The lateral border is the border of the scapula facing the humerus. It’s also close to your armpit, so it’s called “axillary border” as well.
- The superior border, which is the shortest and thinnest.
Bony Features of the Scapula:
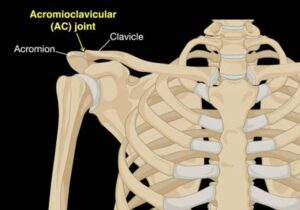
The acromion also articulates with the clavicle and so between the acromion and clavicle there is a joint it’s called the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. It’s a synovial plane joint. The clavicle articulates with the scapula. It allows you to move your arm up and down and the clavicle and scapula label to move your arm so it gets mobility.
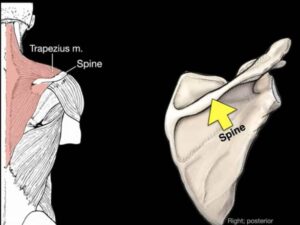
The spine of the scapula has the trapezius muscle that is anchors to give support to the scapula.
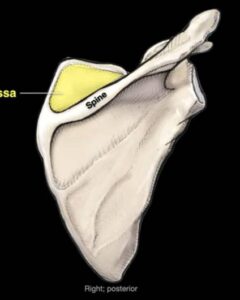
The fossa is a shallow concave surface, so this fossa is on the back of the scapula and above the spine of the scapula so it’s called a supraspinous fossa.
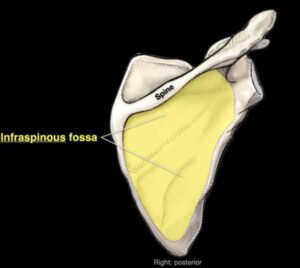
The infraspinous fossa is the fossa below the spine of the scapula.
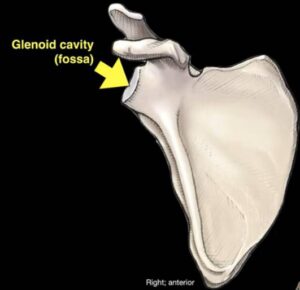
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a part of the shoulder. It is shallow, which is located on the anterior side of the scapula.
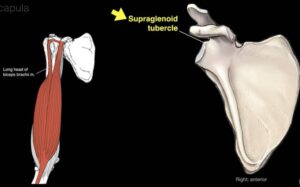
Supraglenoid tubercle has found small projection found at the superior margin of the glenoid cavity. The supraglenoid tubercle is the origin point of the long head of the biceps.
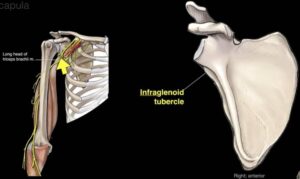
On the inferior margin of the glenoid cavity, you will find the infraglenoid tubercle. This is also an important landmark to remember since the long head of the triceps arises from the structure.
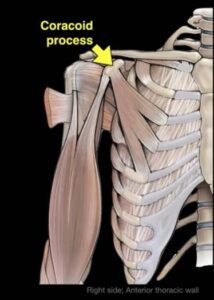
This coracoid process is important for muscle attachment, in fact, three muscles are the pectoralis minor muscle, the short head of the biceps muscle, and the coracobrachialis muscle all have attachments to the coracoid process.
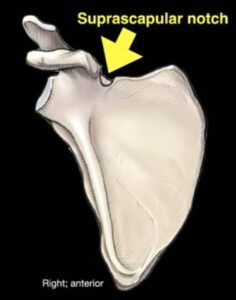
On the suprascapular notch, we have a ligament called the suprascapular ligament that goes across. So, you have the suprascapular artery that goes to the ligament.
If you have any questions about Scapula Anatomy please feel free and leave a comment.
Do share this blog with your friends and family!